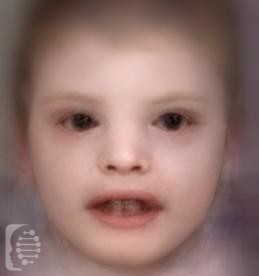
22q11.2 Deletion syndrome
22q11.2 Deletion syndrome, or as it is sometimes referred to, DiGeorge syndrome, is a genetic disorder. It is often referred to by several different names and presents with a wide range of symptoms that can affect almost any part of the body. The characteristics and symptoms of the syndrome vary greatly between individuals and even […]