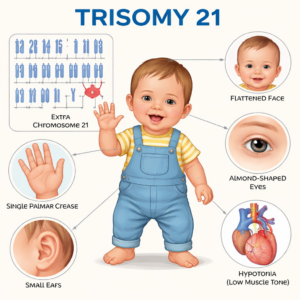
Hello, parents! We’re delving into the fascinating world of genetics; a subject that holds countless mysteries and wonders about how traits and genetic conditions pass from one generation to the next. Genetics might seem like a complex field, but by breaking it down, you can better understand how it affects your family’s health.
What Are Inheritance Modes and Patterns?
When we talk about inheritance in genetics, we’re referring to how certain traits or genetic disorders are passed down from parents to their children. Understanding these modes and patterns is important for assessing risk factors associated with potential genetic disorders.
Why It Matters
- Predicting Disorders: Recognizing how traits are inherited helps anticipate the likelihood of developing certain conditions.
- Informed Decisions: For expectant parents or those planning a family, this knowledge aids in making informed health decisions.
Key Inheritance Modes
Let’s explore the most common modes of inheritance that are used to predict how genetic disorders may be passed on:
1. Autosomal Dominant
How It Works: Only one copy of a mutated gene (from either parent) is needed for the child to exhibit the trait or disorder. Each child has a 50% chance of inheriting the condition.
Examples: Huntington’s disease, and Marfan syndrome. Huntington’s disease, for example, has a nearly 100% penetrance, meaning that if you inherit the gene, you are very likely to develop the disease.
2. Autosomal Recessive
How It Works: Two copies of a mutated gene (one from each parent) are necessary for the child to exhibit the disorder. Each child has a 25% chance of being affected if both parents are carriers.
Examples: Cystic fibrosis, and sickle cell anemia. Cystic fibrosis affects approximately 1 in every 2,500 to 3,500 white newborns.
3. X-Linked Dominant
How It Works: Disorders occur when a mutated gene is located on the X chromosome, affecting both males and females, though often more severe in males.
Examples: Fragile X syndrome.
4. X-Linked Recessive
How It Works: Usually affects males more frequently because they have only one X chromosome. Females can be carriers.
Examples: Hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Duchenne muscular dystrophy affects approximately 1 in 3,500-5,000 newborn males.
5. Mitochondrial
How It Works: Passed from mother to all her children through mitochondrial DNA. It affects energy production in cells.
Examples: Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy.
Understanding Pedigree Analysis
A pedigree chart can be a useful tool to visualize inheritance patterns across generations:
How to Use: Observing family history and looking for trends in the transmission of traits can provide insights into which inheritance mode may be involved.
Tip: Consult with a genetic counselor for accurate analysis.
Practical Tips for Parents
- Genetic Counseling: Consider scheduling a session with a genetic counselor if you have concerns. They can help assess risks and provide recommendations based on family history.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest research and available tests. FDNA resources are great resources for reliable information.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Regardless of genetic predispositions, fostering a healthy lifestyle can mitigate some risks associated with inherited conditions.
How the Family Health Checker app Can Support Parents
Knowing how genetic traits are passed down and other genetic information is essential for early diagnosis and intervention. For parents seeking further insights, FDNA’s Family Health Checker app can be a practical resource. This app facilitates at-home secure AI assessment of developmental and genetic concerns to suggest potential health issues. Parents receive a free report and can connect with healthcare professionals for further evaluation, including a no-cost genetic test for eligible kids. While AI tools can be helpful, consulting a healthcare professional for a formal diagnosis and personalized guidance is essential.
Now that you have a foundational understanding of inheritance modes and patterns, consider taking proactive steps. Whether it’s speaking to a healthcare professional about genetic testing or simply keeping an open dialogue within your family about your health history, you have the power to affect your family’s future well-being.
For a closer look at your family’s genetic background and to explore potential risks, connect with a genetic counselor and consider using tools like the Family Health Checker app from FDNA, which offers AI-supported insights and connects you to healthcare resources, and offer access to no-cost genetic test for eligible users.