What is Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia (CDD Autosomal Recessive)?
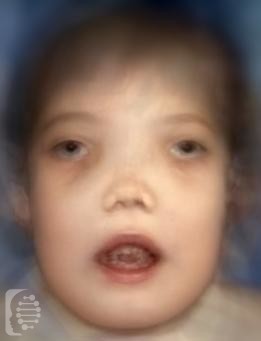
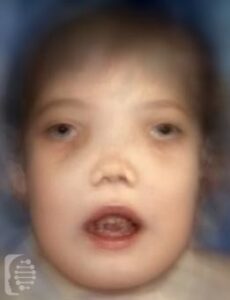
Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia, is a very rare bone disorder where calcium builds up in the skull affecting the facial features of those affected.
Abnormally shaped bones, a hardening of the bones, and excessive overgrowth of the bones characterize the syndrome.
To learn more about Lionitis Disease, also known as Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia, explore our detailed overview on What Is Lionitis Disease?
What gene change causes Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia (CDD Autosomal Recessive)?
The exact causes of this incredibly rare genetic syndrome are as yet unknown. Due to consanguineous families, autosomal recessive inheritance has been suggested.
What are the main symptoms of Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia (CDD Autosomal Recessive)?
The main symptoms of the syndrome are:
- Bone dysplasia: abnormally shaped bones in the head, spine, arms, and legs
- Massive bone sclerosis: hardening of the bones
- Hyperostosis: excessive bone growth in the skull and face
These symptoms then lead to distinct facial features and associated health issues that may reduce the life expectancy of individuals with the syndrome.
Other symptoms of the syndrome include rib abnormalities, short stature, and coarse facial features including frontal bossing ( a very prominent high forehead)
How is it diagnosed?
To find out if someone has a diagnosis of Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia (CDD Autosomal Recessive), it is important to have a consultation and evaluation with a clinical genetic specialist. Specialists may also suggest specific genetic testing or other types of tests to help reach a diagnosis. FDNA’s AI technology can help speed up the diagnostic process by analyzing facial features and other health information.