There are five widely recognized genetic disorders in babies that are currently believed to be the most common. This is either because of their high prevalence or because there is more awareness about these particular genetic disorders.
Down syndrome
This genetic disorder occurs in 1 in every 700 live births in the US, making it one of the most common of the rare genetic syndromes. There are now several types of prenatal genetic screening and testing options for this chromosomal condition. This has increased awareness of this rare syndrome, especially among expectant parents.
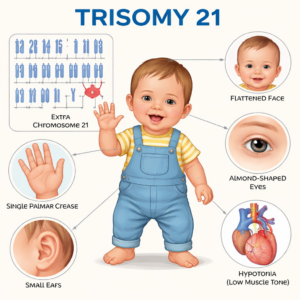
Down syndrome is usually diagnosed before birth, or at birth. This genetic disorder is congenital, meaning it is present at birth. It is the result of the presence of an additional chromosome 21 in affected individuals. It is not an inherited condition, although as with all chromosomal disorders, an older maternal age is believed to be a risk factor.
Common symptoms of Down syndrome include characteristic facial features – almond-shaped eyes, a flat face, and a nose. Other physical features of the syndrome can include low muscle tone (hypotonia), and congenital heart defects. Some individuals with Down syndrome may also have mild-moderate intellectual disability and developmental delay.
While Down syndrome is currently one of the most common genetic disorders diagnosed in babies, this may change in the years ahead. The more popular prenatal genetic screening for Down syndrome becomes, the fewer babies are born with this chromosomal condition. In time it may no longer be one of the most common genetic disorders in babies.
Cystic fibrosis
This genetic disorder is an inherited condition. The gene responsible for causing it must be inherited from both parents. There are around 30,000 people in the US living with Cystic Fibrosis.
Cystic fibrosis affects the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems of those affected. This is due to the build-up of thick and sticky mucus that the disease triggers the production of. Life expectancy is not high with this condition, generally around 33.4 years for males. Many individuals with cystic fibrosis suffer from very serious health and medical conditions.
Tay-Sachs syndrome
Tay-Sachs is a very serious genetic disorder in babies and is most common in babies with two parents who are of Ashkenazi-Jewish descent. Tay-Sachs is usually diagnosed during infancy and life expectancy with this life-threatening condition is usually no more than 2-3 years.
The symptoms of Tay-Sachs include seizures and fits, muscle stiffness, swallowing difficulties, developmental delay and the loss of skills learned before, vision and hearing loss that is progressive, and a floppiness that gets worse with time, often ending in paralysis.
Tay-sachs is caused by mutations in the HEXA gene, located on chromosome 15. This gene change creates a toxic build-up of fatty substances in the cells of those affected, and this in turn triggers the symptoms of this syndrome.
Genetic screening and diagnosis
Recent years have seen significant advancements in the development of new and more accurate prenatal genetic screening tests that make it possible to identify an unborn child’s risk for developing a genetic disorder. These tests, including NIPT testing and chorionic villus sampling, are raising awareness about genetic disorders in babies. This awareness is important to improve the accuracy of genetic diagnosis and testing in babies.