Causes
Chromosomal abnormalities are the cause of many rare diseases and other inherited diseases. These rare diseases often present with multiple symptoms, some of them congenital and present at birth, while others may develop later in childhood or adulthood.
There are two main types of chromosomal abnormalities -numerical and structural.
What are numerical chromosomal abnormalities?
Each of the cells in the body contains 46 chromosomes, of which there are 23 pairs.
The most common form of a numerical chromosomal abnormality is when there is an extra chromosome or a missing chromosome in the body’s cells.
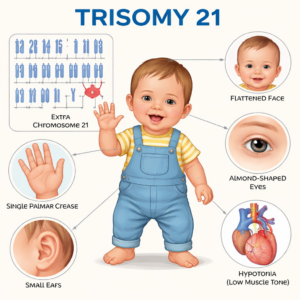
One of the most common chromosomal abnormalities, both in terms of prevalence and visibility, is Down syndrome or Trisomy 21 as it is otherwise known. Individuals with Down syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21 and as a consequence 47 chromosomes.
Another common chromosomal abnormality is Turner syndrome. This rare disease is caused by a missing X chromosome, leaving individuals with just 45 chromosomes instead of 46.
What are structural chromosomal abnormalities, and what causes them?
Structural chromosomal abnormalities occur when the length of the chromosome – and its two arms, the short (p), and the long (q) are altered, usually with an abnormal length, due to the unusual location of the centromere. The structure of the chromosome is essentially altered and this creates a chromosomal abnormality which can cause the development of a rare disease.
Common chromosomal abnormalities
Some of the main chromosomal diseases are:
- Down syndrome, Trisomy 21
- Edward’s syndrome, Trisomy 18
- Patau syndrome, Trisomy 13
- Cri-du-chat syndrome, 5p minus syndrome
- Wolf-Hirschorn syndrome, deletion 4p syndrome
- Klineflelter syndrome, extra X chromosome in males
Genetic testing and diagnosis for chromosomal abnormalities
The most common form of genetic testing for chromosomal abnormalities is karyotyping. This involves studying an individual’s chromosomes under a microscope to understand if there are identifiable extra or missing chromosomes, or any changes in the structure of the chromosome as well. However, this is not able to identify the specific area where the deletion occurs, for example.
A more detailed form of genetic testing for chromosomal abnormalities is known as microarray analysis. This type of genetic testing uses a molecular approach to identify genetic markers or small stretches of DNA. This can identify the exact part of the chromosome which is missing or altered in some way.
Genetic counseling for chromosomal abnormalities
Genetic testing is an essential support service for anyone undergoing screening or testing for chromosomal abnormalities. It is an important service that empowers potential rare disease patients and their families as they navigate their diagnostic journey. Genetic counseling can help individuals understand the types of testing for chromosomal abnormalities, the process for each, and the potential results of each type of testing. They will be able to explain what a diagnosis of a chromosomal abnormality might mean, and what rare disease it might place an individual at risk for.